Table Of Content
Review existing literature to identify similar studies and their research designs, which can serve as a guide. Ultimately, the chosen research design should align with your research questions, provide the necessary data to answer them, and be feasible given your own specific requirements/constraints. In an experimental design, the researcher actively tries to change the situation, circumstances, or experience of participants (manipulation), which may lead to a change in behavior or outcomes for the participants of the study. The researcher randomly assigns participants to different conditions, measures the variables of interest, and tries to control for confounding variables.
The Four Types of Research Design
Observational clinical study is a study in which knowledge from treatment of persons with drugs is analysed using epidemiological methods. In these studies, the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring are performed exclusively according to medical practice and not according to a specified study protocol.[9] They are subclassified as per Figure 2. Expert opinion, experience, and authoritarian judgement were the norm in clinical medical practice. At scientific meetings, one often heard senior professionals emphatically expressing ‘In my experience,…… what I have said is correct!
Are we on the cusp of a fourth research paradigm? Predicting the future for a new approach to methods-use in medical ... - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Are we on the cusp of a fourth research paradigm? Predicting the future for a new approach to methods-use in medical ....
Posted: Wed, 14 Nov 2018 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Consider your aims and approach
Examples of descriptive studies include a survey of dietary habits among pregnant women or a case series of patients with an unusual reaction to a drug. An exploratory design is conducted about a research problem when there are few or no earlier studies to refer to or rely upon to predict an outcome. The focus is on gaining insights and familiarity for later investigation or undertaken when research problems are in a preliminary stage of investigation.
OTHER RESEARCH METHODS

A Navaho (Diné) tribesman and carpenter, Benally comes to us from the mountains of Red Valley and Oak Springs, Arizona. After graduating from tribal high school, he found himself building off-road electric vehicles at a Utah State University lab led by Professors Curtiz Frazier and Jared Barrett. Two years later, in 2017, he transferred to the University of Minnesota and accepted a Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) through the NSF-funded Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC) at the University. During this time, he worked with Professor Vlad Pribiag (School of Physics and Astronomy) building nanoelectronic devices in the cleanroom for Majorana fermion research. He returned to the MRSEC REU in summer 2018 and this time he worked with Wang on micro and nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions for classical computer memory and logic applications.
They would then be bale to determine whether students in smaller classes perform at any different rate, on average, compared to larger class groups. If there is a difference, they may be able to demonstrate a causal relationship between classroom size and academic performance. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations.
Before collecting data, it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure. You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study. A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc.
A longitudinal study is a type of study in which the same variables are observed repeatedly over a short or long period of time. It’s usually observational research, although it can also take the form of a long-term randomized experiment. By the term ‘research‘, we can understand that it’s a collection of data that includes critical information by taking research methodologies into consideration. In other words, it is a compilation of information or data explored by setting a hypothesis and consequently coming up with substantive findings in an organised way.
Lived experience research as a resource for recovery: a mixed methods study - BMC Psychiatry - BMC Psychiatry
Lived experience research as a resource for recovery: a mixed methods study - BMC Psychiatry.
Posted: Mon, 21 Sep 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The advantages of this approach are its sensitiveness to the context, the rich and nuanced understanding it generates, and minimal respondent bias. However, this is also an extremely time and resource-intensive approach, and findings are specific to a given culture and less generalisable to other cultures. Case research is an in-depth investigation of a problem in one or more real-life settings (case sites) over an extended period of time. Data may be collected using a combination of interviews, personal observations, and internal or external documents. Case studies can be positivist in nature (for hypotheses testing) or interpretive (for theory building). The strength of this research method is its ability to discover a wide variety of social, cultural, and political factors potentially related to the phenomenon of interest that may not be known in advance.

Cross-sectional study
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting. In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from. Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world.
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context. Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes.
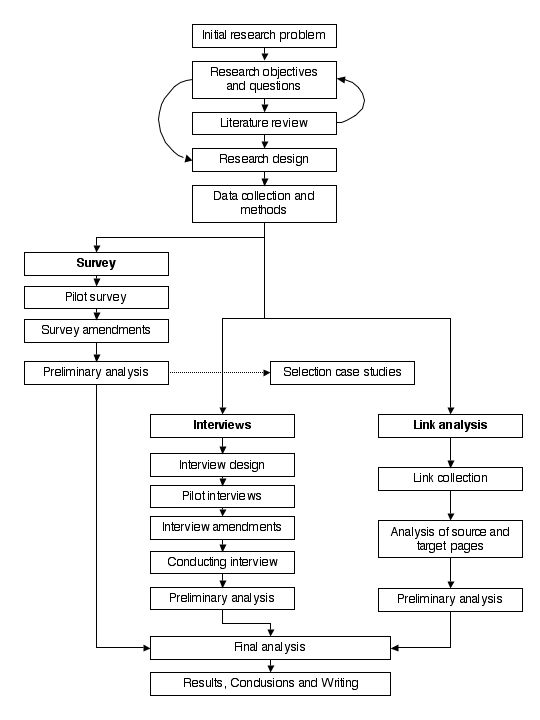
The study focuses on how the teacher and students adapt to the new method, conducting semi-structured interviews with the teachers and students. While the study provides specific and detailed insights of the teaching method in that classroom, it cannot be generalized to other educational settings, as statistical significance has not been established to achieve generalization. A correlational research design is used when researchers want to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, but it does not necessarily mean that one variable causes changes in the other (Marczyk, DeMatteo & Festinger, 2010). A research design is defined as the overall plan or structure that guides the process of conducting research. It is a critical component of the research process and serves as a blueprint for how a study will be carried out, including the methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data.
Clinical studies include observational studies and interventional studies and are subclassified as in Figure 2. A blueprint of the procedure that enables the researcher to maintain control over all factors that may affect the result of an experiment. In doing this, the researcher attempts to determine or predict what may occur.
A Research Design is simply a structural framework of various research methods as well as techniques that are utilised by a researcher. Observational studies can be subdivided into cohort, case–control, cross-sectional and ecological studies. You can collect historical data from an assortment of sources if combining the data helps you get to your desired study results. While there are many types of research design, some elements are essential to all types. For your research to be impactful, pay special attention to keeping the margin of error minimal.
This article takes a look at some common distinctions made between different types of research and outlines the key differences between them. Observational studies can be either descriptive (nonanalytical) or analytical (inferential) – this is discussed later in this article. This helped uncover key reasons for poor performance and guided changes in packaging. Carma Laboratories worked with research company MMR to measure customers’ reactions to the lip-care company’s packaging and product.
A properly conducted systematic review presents the best available research evidence for a focused clinical question. The review team may obtain information, not available in the original reports, from the primary authors. The strength of a systematic review lies in the transparency of each phase and highlighting the merits of each decision made, while compiling information. The function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence obtained enables you to effectively address the research problem as unambiguously as possible.


No comments:
Post a Comment